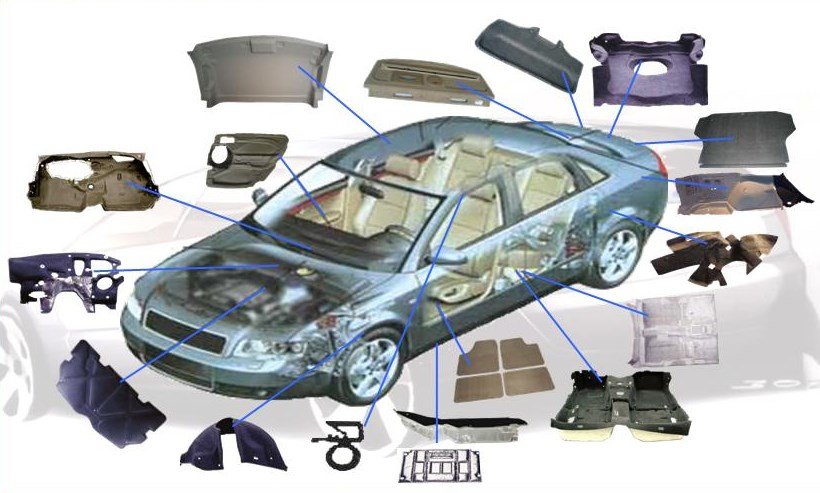
Thermoforming
Thermoformed parts are widely used in packaging, medical devices, automotive components, consumer appliances, and industrial products. They offer lightweight, cost-effective, and customizable solutions for high- and mid-volume production. Key benefits include rapid manufacturing, design flexibility, and material efficiency. Challenges include regulatory compliance, precision requirements, and durability in demanding environments.
Thermoforming is often preferred over other production methods due to its lower tooling costs, faster lead times, and suitability for producing large, lightweight parts. It offers greater design flexibility and supports a wide range of materials, including sustainable and recycled plastics. The process delivers high-quality surface finishes and simplifies secondary operations like trimming and assembly.
Thermoforming also generates less production waste and can be easily automated for higher-volume manufacturing. These advantages make it ideal for industries such as packaging, automotive, appliances, and medical devices, especially when cost-efficiency, speed, and design adaptability are important.

Industry Trends
Over the last 20 years, thermoforming has shifted toward sustainable materials, automation, and precision. Its use has expanded from basic packaging to high-performance parts in automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors. Demand for customization and short-run production has grown, driven by market shifts and just-in-time manufacturing. The medical field has seen major adoption, requiring cleanroom and traceable processes. These trends reflect evolving technology, environmental concerns, and more diverse application needs.
"Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of high intention, sincere effort, intelligent direction and skillful execution; it represents the wise choice of many alternatives."

Objectives and challenges in QA for thermoformed parts
Quality assurance is critical for thermoformed parts to ensure dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and compliance with industry standards. It helps detect defects early, reduces waste, and ensures consistent performance—especially in packaging, medical, and automotive applications where precision, safety, and customer satisfaction are essential to success and brand reputation.
Consider the following goals, and the wide variety of flaws that can occur in the finished product.
 |
Dimensional Accuracy ensures that the part meets design specifications and fits with mating components in an assembly. |
|
 |
Wall Thickness Consistency affects part strength, functionality, and material usage. Thin spots can cause failure under stress. |
|
 |
Surface Finish / Aesthetics impacts the visual appeal, brand perception, and in some cases, functional (e.g., smoothness for hygiene or aerodynamics). |
|
 |
Material Integrity ensures structural performance and longevity. Defects like thinning, burns, or bubbles can compromise strength. |
|
 |
Trimming Accuracy impacts final geometry. Misaligned or uneven trims can lead to functional issues or part rejection. |
|
 |
Cooling Control prevents warping or internal stresses, affecting dimensional stability and aesthetics. |
|
 |
Color and Material Consistency are important for aesthetic matching, UV resistance, and compliance in regulated industries (e.g., food packaging, medical). |
|
 |
Adherence to Regulatory Standards is critical in industries (medical, food, automotive) with strict QA and compliance requirements. |
|
 |
Process Repeatability ensures consistent quality over large production runs, which reduces scrap and increases efficiency. |
|
 |
Mold Fit and Venting for proper vacuum seal and venting are critical for accurate replication of the mold’s shape and fine details. |
|
2D vs 3D Solutions
A 3D inspection system offers significant advantages over traditional 2D vision systems when detecting defects in thermoformed or other complex parts. Here are key ways 3D inspection can outperform 2D:
3D Imaging...
2D Imaging...
Improper Tool Contact or Mold Inconsistencies
Repeatability and Accurate Comparisons
Conclusion
Ajile Depthscan 3D Imaging Systems incorporate multi-camera and multi-view stitching for full coverage of parts, enabling detailed inspection of any size or shape of part. Ajile workflow automation and plugins for industry standard GD&T inspection software save time, increase throughput, and catch defects early before they result in material waste.